HIV
MOST COMMONLY USED VOCABULARY IN RELATION TO HIV/AIDS
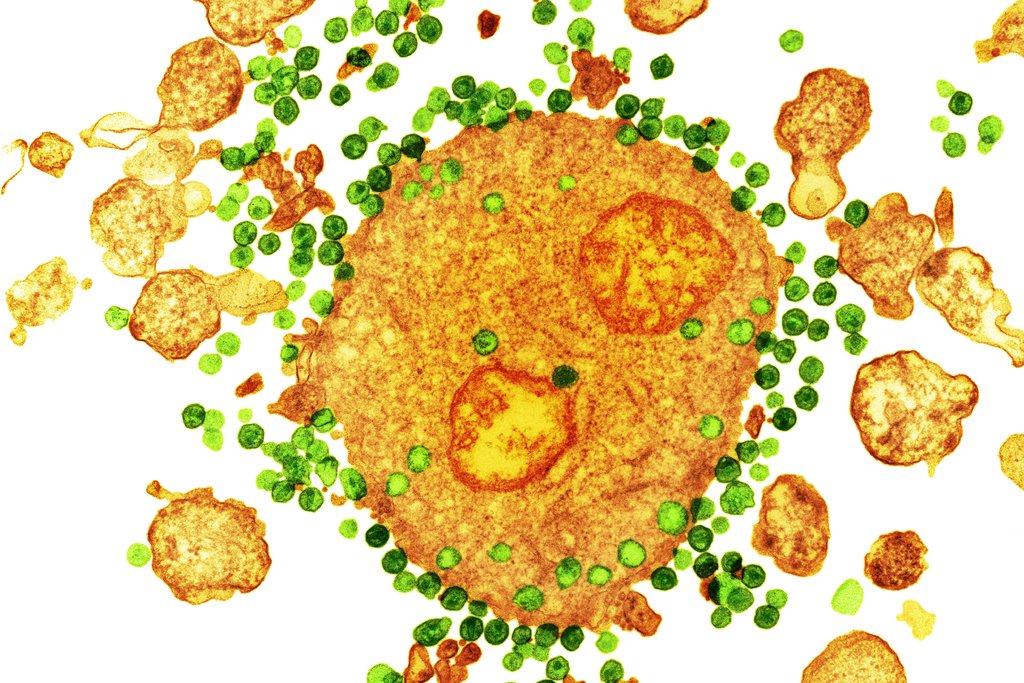
Immune System – defense system, or a collection of cells which are found in blood and human organs; their main function is to fight against external microorganisms that attack human organism. Healthy immune system makes our body resistible to a large number of infections; Immune Deficiency – a condition characterized by a weakness of the immune system which causes its malfunction, that is, the immune system is no longer capable of protecting the body against infections; HIV – Human Immune Deficiency Virus; HIV+ - presence of HIV in the blood of the person confirmed by suitable HIV tests; HIV− - non-existence of HIV in the blood of the person confirmed with suitable HIV tests; HIV Tests – a combination of tests for acknowledgment of the existence of antibodies for HIV in the blood. First of all, two ELISA tests (immune-enzyme tests for the existence of antibodies for HIV) are conducted, and if both are HIV+ a third verification test is carried out, the Western blot test. AIDS/HIV – Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome; syndrome in medicine refers to a combination of symptoms (signs) of a certain disease. It is characterized by general signs of infection which the HIV virus can cause, such as high temperature, diarrhea, nausea and the like. AIDS refer to a condition marked by a decrease of a certain class of white blood cells (CD 4 T-Ls) below a certain number/value; it is a condition in which the immune system of the human organism becomes susceptible to a lot of infections. Opportunistic infections – infections, such as bacterial, viral, parasitical, and fungal infections as well as neo-plastic (tumor) processes, that attack the human organisms and cause the clinical condition of AIDS (most of the infections are such that cannot attack an organism with healthy immune system); Ways of HIV virus transmission: 1. Blood and blood products: Blood - Blood contact between two people (open wounds, use of the same needles and syringes among intravenous drug users, untested blood transfusion); Blood products – transfusion of untested blood plasma, blood cells etc. (Transfusion is no longer considered as a way of virus transmission because each blood unit is tested for HIV); 2. Sexual way - The most common way of virus transmission today is the unsafe sexual intercourse (vaginal, anal and oral sex); 3. Mother-child A pregnant woman having the virus can infect the baby through the placenta. That is why pregnancy is a contraindication for HIV+ women. An HIV+ mother who breastfeeds her baby can transmit the virus through her milk. HIV Testing: 1. Clinic for Infectious Diseases and Febrile States 2.State Health Care Institute 3. Clinical Biochemistry Institute 4. HIV/AIDS Information and prevention